
/Bohr-58e690203df78c51620ff02e.jpg)
His essay, which he submitted at the last minute, won the prize. He went beyond the original task, incorporating improvements into both Rayleigh's theory and his method, by taking into account the viscosity of the water, and by working with finite amplitudes instead of just infinitesimal ones. To complete his experiments, he had to make his own glassware, creating test tubes with the required elliptical cross-sections.
#Niels bohr atomic model 3d series#
Bohr conducted a series of experiments using his father's laboratory in the university the university itself had no physics laboratory. This involved measuring the frequency of oscillation of the radius of a water jet. In 1905 a gold medal competition was sponsored by the Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters to investigate a method for measuring the surface tension of liquids that had been proposed by Lord Rayleigh in 1879. He also studied astronomy and mathematics under Professor Thorvald Thiele, and philosophy under Professor Harald Høffding, a friend of his father. His major was physics, which he studied under Professor Christian Christiansen, the university's only professor of physics at that time. In 1903, Bohr enrolled as an undergraduate at Copenhagen University. īohr was educated at Gammelholm Latin School, starting when he was seven. Niels was a passionate footballer as well, and the two brothers played several matches for the Copenhagen-based Akademisk Boldklub (Academic Football Club), with Niels as goalkeeper. Jenny became a teacher, while Harald became a mathematician and footballer who played for the Danish national team at the 1908 Summer Olympics in London. He had an elder sister, Jenny, and a younger brother Harald. Niels Henrik David Bohr was born in Copenhagen, Denmark, on 7 October 1885, the second of three children of Christian Bohr, a professor of physiology at the University of Copenhagen, and his wife Ellen née Adler, who came from a wealthy Jewish banking family. He was involved with the establishment of CERN and the Research Establishment Risø of the Danish Atomic Energy Commission and became the first chairman of the Nordic Institute for Theoretical Physics in 1957. After the war, Bohr called for international cooperation on nuclear energy. From there, he was flown to Britain, where he joined the British Tube Alloys nuclear weapons project, and was part of the British mission to the Manhattan Project. In September 1943 word reached Bohr that he was about to be arrested by the Germans, so he fled to Sweden. After Denmark was occupied by the Germans, he had a famous meeting with Heisenberg, who had become the head of the German nuclear weapon project.
Later, the element bohrium was named after him.ĭuring the 1930s, Bohr helped refugees from Nazism. He predicted the existence of a new zirconium-like element, which was named hafnium, after the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered.

Bohr mentored and collaborated with physicists including Hans Kramers, Oskar Klein, George de Hevesy, and Werner Heisenberg. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy.īohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen, now known as the Niels Bohr Institute, which opened in 1920.
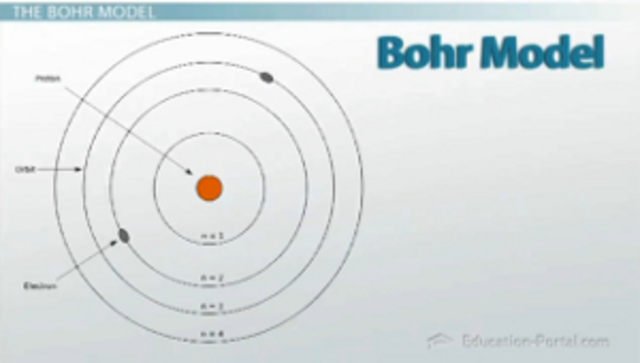
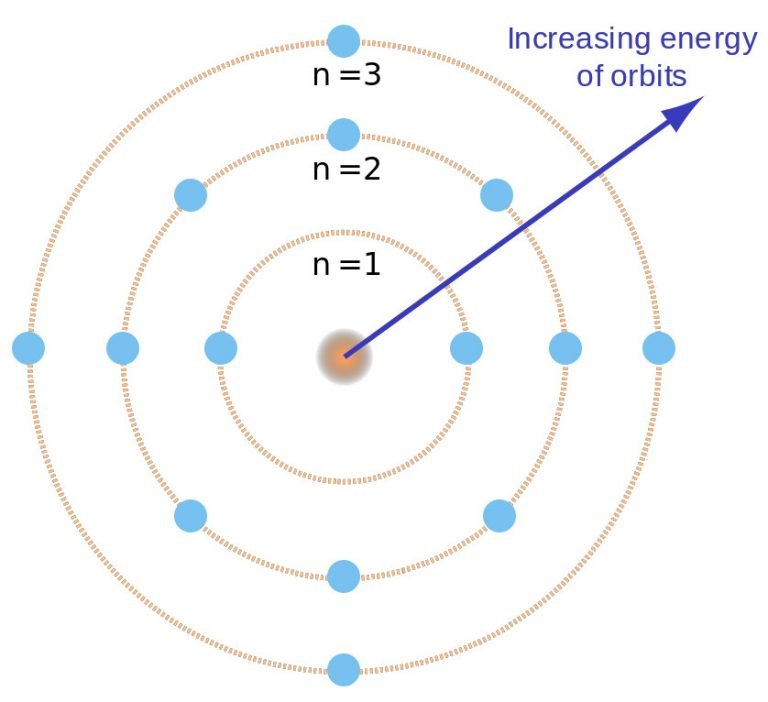
He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research.īohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Niels Henrik David Bohr ( Danish: 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
